Automated Tests – Behaviour-Driven Development
Software development involves a number of activities that are very prone to bugs. That’s why software automated tests are crucial to identify faults and evaluate the product quality.
The following article describes the fundamentals of the Behaviour-Driven Development (BDD) methodology and a study about Cucumber, the tool used to implement it.
Quality in Context of Agile Methods
The deployment of agile methods have been ensuring the flexibility expected in the organizations’ processes, such as planning, efficiency and communication among teams.
In this regard, not only quality has become more and more important, but also the understanding of new functionalities and the capacity of making teams aware of the need of integrating quality and development efforts.
Accordingly, when the implementation of the BDD testing approach makes use of agile methods, the best results are achieved, avoiding rework and behaviour bugs in the development process.
What is BDD?
Behavior-Drive Development (BDD) is a software development approach intended to define the specifications of the software’s several behaviour layers using automated tests.
Created by Mr. Dan North around 2003, the term was coined to solve limitations in the Test-Driven Development (TDD). According to the BDD approach, it’s necessary to define the behaviour of a feature before implementing it.
The primary purpose of the BDD methodology is to facilitate the understanding of objectives so that all stakeholders are aware of what is being delivered, creating testable and automated behaviours and adding value for users before developing a source code. They avoid behaviour-based bugs and generate a set of regression tests based on them.
Methodology
According to the agile development cycle, the first step to start the analysis of stories in the Cucumber structure is to identify the acceptance criteria and capture testing scenarios.
Acceptance Criteria:

The specification written in natural language interpreted by Gherkin will serve as an implementation model for the development and quality teams in the Cucumber structure.
Automated Tests
The BDD allows to focus on the efforts designed to evolve the requirements so that changes are effective.
Designed with the BDD approach, the adjustments to the business objectives require a high level of understanding.
Test Scenarios:
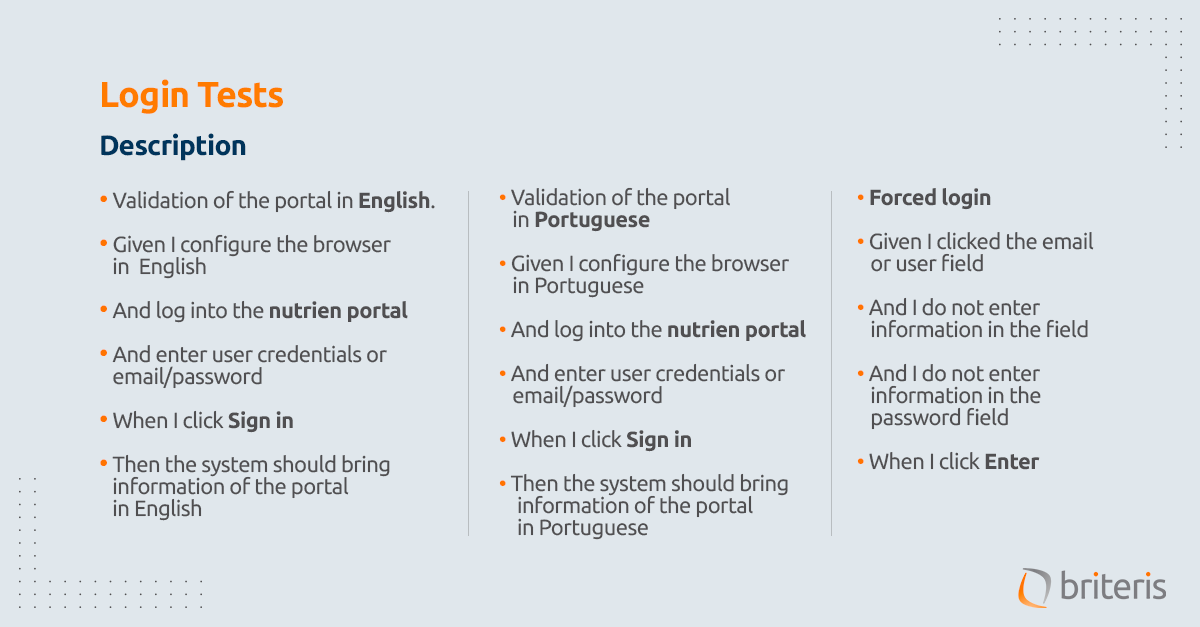
Ruby
Ruby is an interpreted open-source programming language which focuses on simplicity and productivity. It has an elegant syntax that is natural to read and easy to write, highly portable and that runs in all main operating systems.
The Ruby Gems software allows you to install and use Ruby software packages in the system and extend or modify functionalities in Ruby applications.
To implement Ruby automated classes, we will use the Gems listed below:
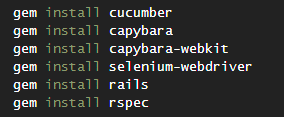
Lista Básica de GEMS
Cucumber
Cucumber is a free tool that supports the BDD written in Ruby and that combines functional specification and acceptance test automation.
The language Cucumber understands is called Gherkin, a business-readable and Domain-Specific Language (DSL). It describes the software’s behaviour without detailing how that behaviour is implemented.
Cucumber is primarily used to develop acceptance tests for apps. When it’s used only for automation purposes, it can be costly.
Here are some points of attention to get the most of the tool:
- Encourages communication with the Product Owner;
- Combines specification and automated tests;
- Ensures that the behaviour’s specifications are easy to read.
The structure in Portuguese is available in Ruby’s 1.9.3 version and later and includes a list of more than 50 supported languages. To configure a feature in Portuguese, you only need to add the following line at the beginning of the file: # language: pt
Cucumber Structure in Portuguese

At this stage, the several benefits of adopting a behaviour-oriented approach, segmenting the behaviours in features and describing the scenarios are noticeable.
Keywords have a special meaning in test automation tools. To list Cucumber’s keywords in Portuguese, type the following command line: cucumber i18n pt
The main keywords used by Cucumber and their respective meanings are:
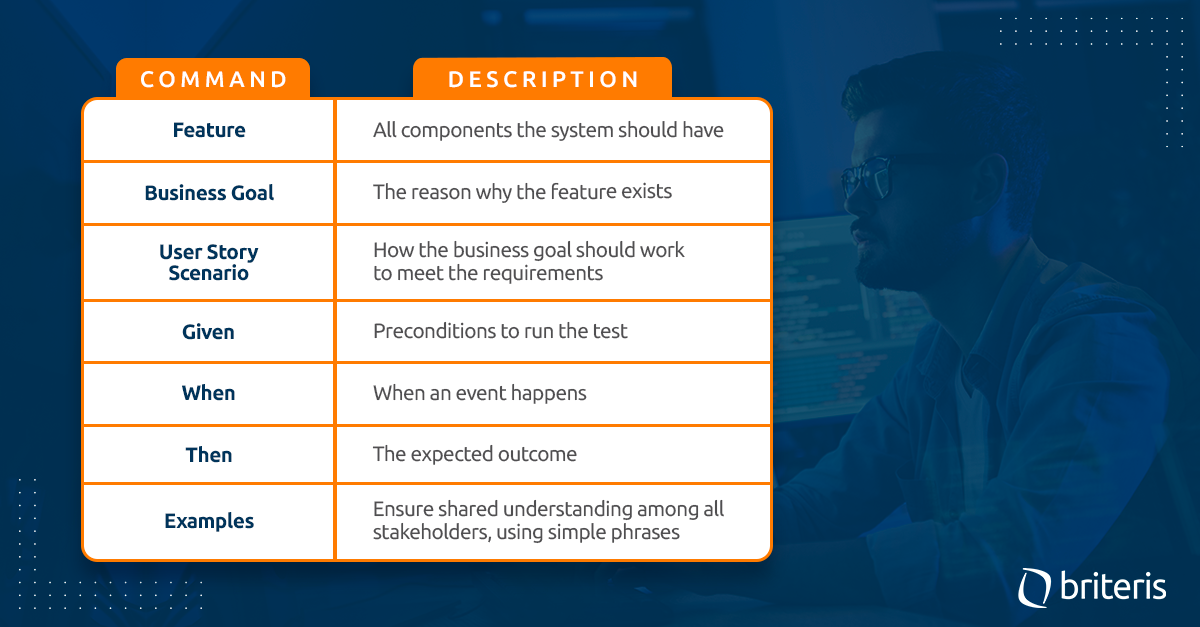
Another very interesting tip is the filter to select the examples associated with a specific business goal. Such examples are of utmost importance because they will serve as parameters to validate if logic is behaving as expected.
Automated Acceptance Criteria
Automated acceptance criteria are validated using Ruby’s and Rspec’s external tools, which control test runs.
After exporting Cucumber tests, they should be organized and the environment and tools should be configured to recognize Cucumber’s features. Machine installation and preparation can be done in any Linux and Microsoft platform.
Running Tests
The environment should be ready before you run a test. Therefore, any error in the running environment can result in the installation of dependencies.
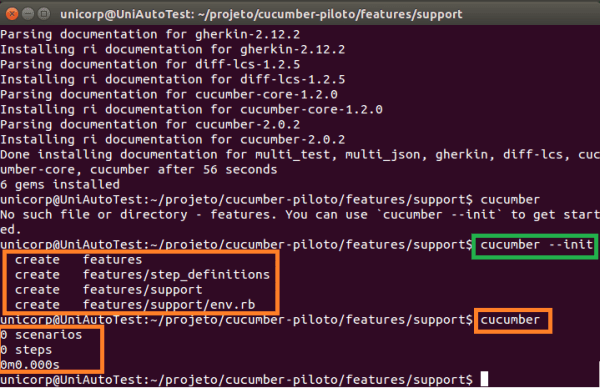
The first step is to run the cucumber-init in the root directory. With this command, the directories recognized by the structure will be automatically created.
Creation of Cucumber directories:
The test implemented in the Cucumber tool will be saved with the name Login.Feature in the features folder until it is recognized by Cucumber.

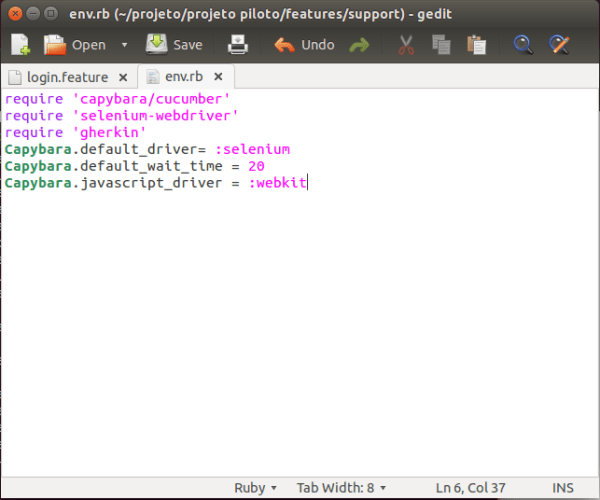
After that, in the support directory, settings should be configured in the env.rb file, where the libraries used will be defined.
Configuring ENV.RB files:
When the Cucumber command is run in the terminal, the following results will be shown:

Steps to be implemented
A new file should be created. This new file, called login.rb, should have two configuration lines.
Configuration lines
The Cucumber runs based on Regular Expressions (regex) and characters, such as / ^ $ /, are very common.
Accordingly, we will substitute the phrase “pending # express the regexp above with the code you wish you had” with gem capybara’s commands.
Capybara basic commands are:

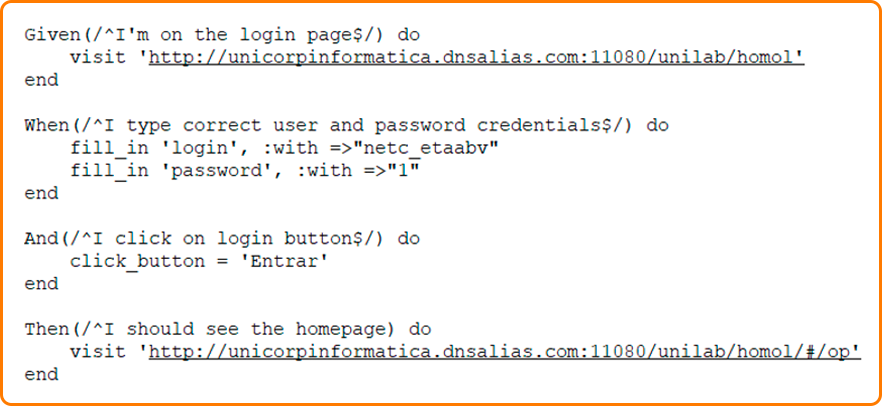
Accordingly, the PAI Capybara implemented in the login.rb feature will be ready to be executed with Ruby.
API Implemented Caybara
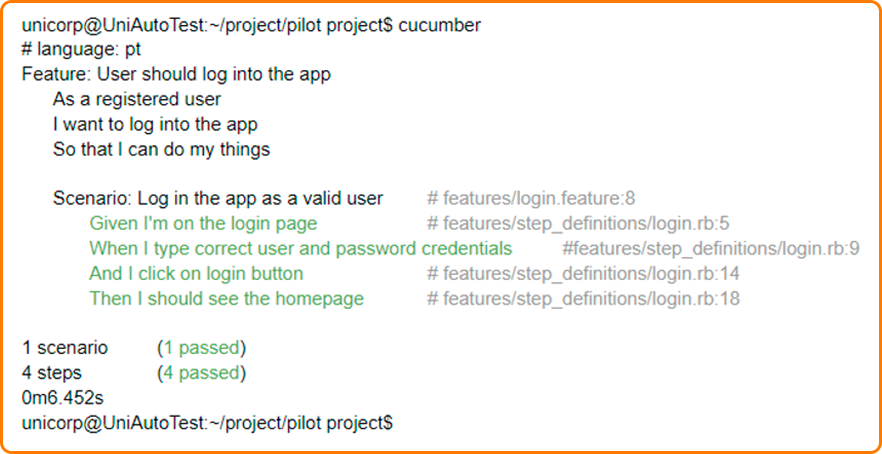
To check the test result, you should type the Cucumber command in the terminal:
Result of the scenarios:
Final Considerations
The development of automated scenarios is a simple and convenient approach that prioritizes quality to return the best results and monitoring during execution.
With BDD, developers write better code and the quality assurance team and product owners work in line with the business objectives.
Therefore, the BDD methodology provides organizations with a new culture that, ultimately, translates into credibility and customer satisfaction.

